Do you have a lump in your neck? Behind or behind your ear, here’s what you need to know
Lumps can develop in the neck area or behind the ear, with causes ranging from benign skin issues like acne to more serious conditions such as tumors.
What are the common causes of these lumps?
Causes of neck lumps:
- Neck cancer
- Tumor in the neck
The presence of a lump or mass in the neck is common among adults and can have various origins.
A neck mass, regardless of size, could indicate an infection or signify a serious health concern. While not always indicative of cancer, additional evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of neck mass formation:
- Viral or bacterial infections, including ear or sinus infections, tooth infections, sore throats, mumps, or goiters, may result in a neck lump, which usually resolves with the disappearance of the infection.
- Noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant) tumors, such as squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, lymphoma, thyroid or salivary gland cancer, skin cancer, or metastatic cancer from other body parts.
Swelling in the back of the neck:
Refer to the previous paragraph.
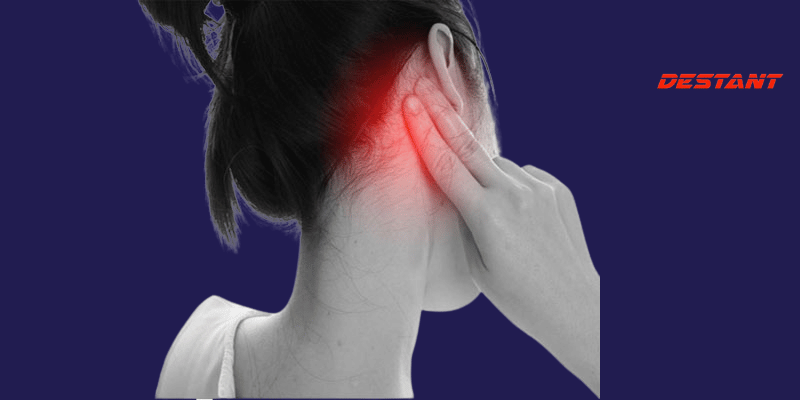
Tumor behind the ear:
Lumps behind the ear can stem from various causes, mostly benign but occasionally indicating a more severe condition. Such lumps may vary in texture and pain sensitivity.
Common causes include colds, flu, sore throats, or respiratory infections, leading to swollen and inflamed lymph nodes behind the ears. In most cases, swollen glands are harmless and resolve spontaneously, often treated with antibiotics if caused by bacterial infections. Mastoiditis, a severe bacterial infection affecting the mastoid bone behind the ear, necessitates immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
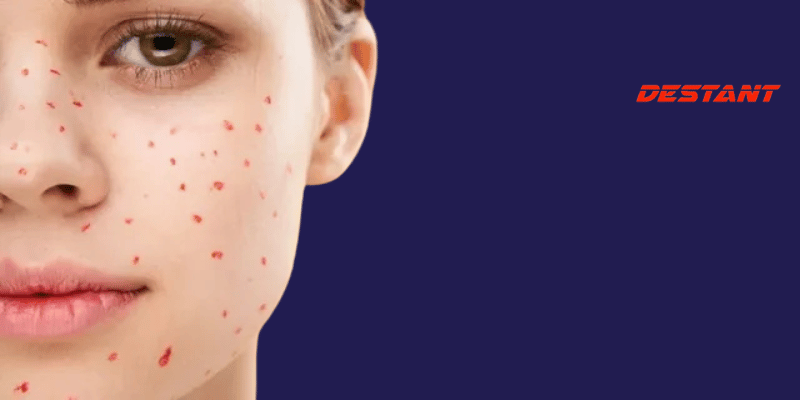
Skin diseases, benign masses, and ear-area masses:
Aside from infections, various skin issues like acne, lipomas, and cysts can lead to lumps behind the ear. While most are painless and self-resolving, infections may require antibiotic treatment. Surgical removal might be necessary for uncomfortable lipomas.
Could an ear lump indicate cancer?
Although rare, some ear lumps may be tumors, with most being benign. Solid, immobile, or irregularly shaped lumps may raise suspicions of cancer. Prompt medical consultation is crucial if the lump is painful, sudden, or accompanied by other symptoms.
Swelling beneath the ear in the neck:
Refer to earlier sections.
What steps should be taken upon noticing a neck or ear lump?
- Evaluation for cancer:
Some neck lumps might be linked to nasopharyngeal cancer, spreading to neck lymph nodes. Prompt medical assessment is essential, especially if accompanied by symptoms like hearing loss, nasal congestion, nosebleeds, blurred vision, facial pain, numbness, or headaches.
Concerning ear-area lumps, they could indicate cancerous tumors like skin cancer or benign growths, potentially increasing in size over time. Regardless of size or pain level, consulting a doctor is imperative for proper evaluation and determining the need for treatment or removal.
Furthermore, ensure a thorough examination of the lymphatic system, as enlarged lymph nodes may signal underlying health issues, including infections or cancer. Consult a doctor if enlarged or swollen lymph nodes are observed, regardless of location.
Lastly, consider the possibility of sebaceous cysts as a cause for lumps at the neck or behind the ears. Seeking medical advice is crucial for accurate diagnosis and determining appropriate treatment options.
If you notice any lumps in your neck or behind your ear, it’s important to see a doctor promptly for further evaluation and diagnosis.