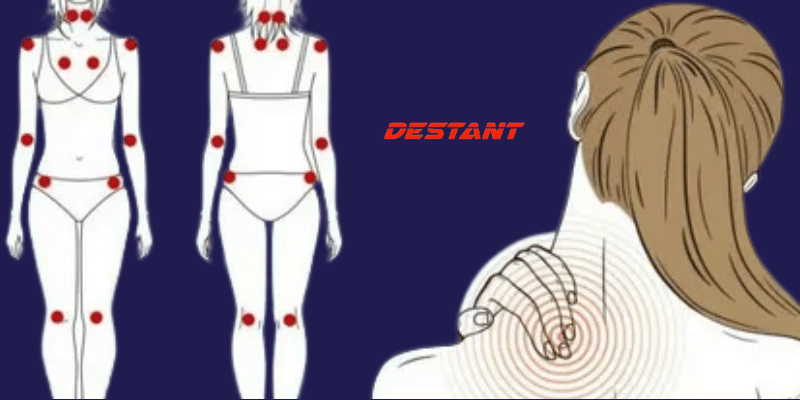
Signs of fibromyalgia you should be aware of
Fibromyalgia Overview:
Definition: A chronic condition affecting the musculoskeletal system, characterized by widespread pain, insomnia, fatigue, and memory problems, with a possible association with depression.
ICD-10 code: M79.7
Types of pain associated with fibromyalgia:
Chest pain: May mimic a heart attack, with sharp, stabbing pain originating in the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum.
Back pain: Usually mild and painful, similar to pain resulting from muscle strain or arthritis.
Leg pain: Felt in the muscles and soft tissues, including a deep, throbbing pain or burning sensation.
Symptoms of fibromyalgia:
Diffuse pain: Dull, aching pain that lasts for at least three months, spreading to both sides of the body and above and below the waist.
Fatigue: constant fatigue, even after adequate sleep.
Cognitive difficulties: “fibro fog” that affects concentration, attention, memory lapses, and alertness.
Other symptoms: lower abdominal pain or dull ache, dry eyes, bladder problems, mood and energy swings.
Fibromyalgia and autoimmunity:
Symptoms overlap with autoimmune diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis), but there are no autoantibodies or evidence of inflammation in fibromyalgia.
Possible causes of fibromyalgia:
Previous injury: triggers symptoms of fibromyalgia.
Infections: Epstein-Barr virus, influenza viruses, shigella, and salmonella may contribute.
Physical and mental trauma: Develops in people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Long-term stress: Prolonged stress on the body can lead to fibromyalgia.
Treatment and management:
There is no cure: Fibromyalgia is incurable, but treatment focuses on reducing pain and improving quality of life.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, antidepressants, antiepileptics, muscle relaxants, and fatigue medications.
Physical therapy: Exercises to improve muscle strength, range of motion, and pain control.
Stress reduction: Managing stress through techniques to reduce the triggers of symptoms.
Lifestyle and Nutrition Recommendations: Correct posture, exercise, balanced diet, avoidance of trigger foods, Ayurvedic techniques, massage therapy, and mind-body exercises such as yoga and tai chi.
Although there is no cure, a multifaceted approach that includes medications, lifestyle changes, and holistic therapies can help manage fibromyalgia symptoms and improve the overall health of individuals affected by this difficult condition. Individualized treatment plans are essential to effectively address the diverse symptoms and experiences associated with fibromyalgia.